Industrial Augmented Reality Glasses: Use Case and Applications
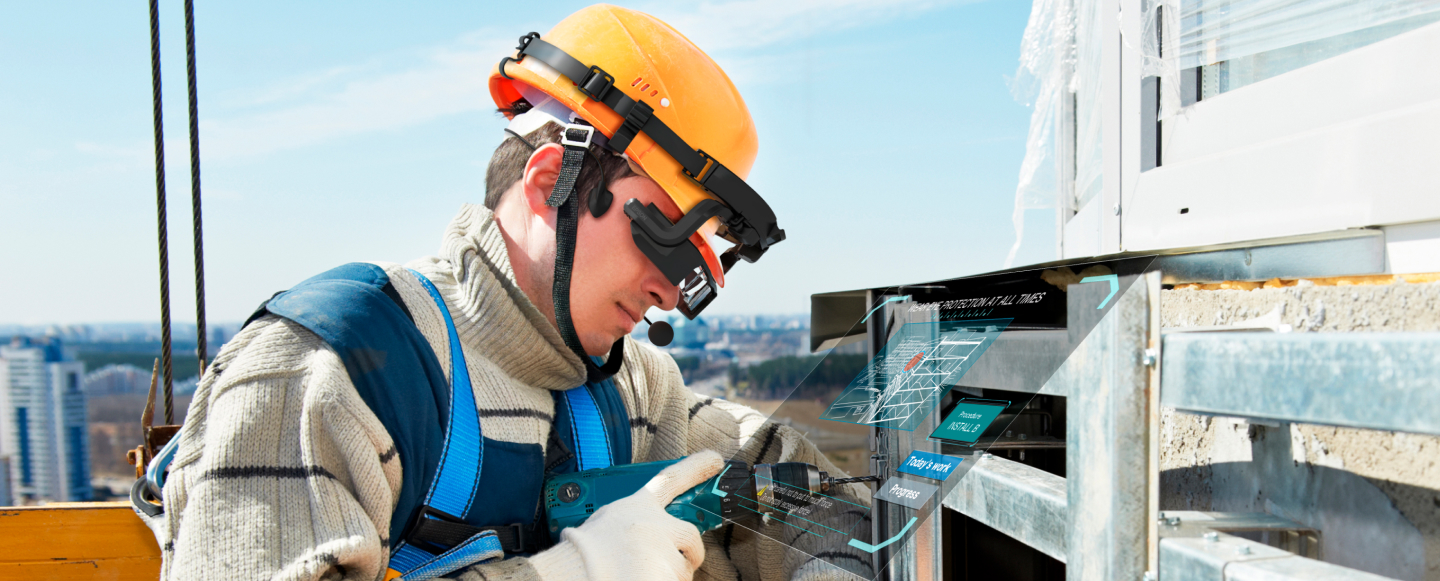

The evolution of smart glasses
We heard about smart glasses around 2013 when Google launched its first version of AR-assisted smart glasses, Google Glass. It seemed like AR technology had found the perfect hardware to deliver all manner of experiences to users. Several other products, including heavy hitters such as Microsoft and Amazon, entered the market in the following years. Innovations kept coming, but manufacturers were still searching for killer apps to mainstream the technology. Then, in 2017, Google relaunched Google Glass, specifically targeting the enterprise market, and was soon followed by other manufacturers who hoped to make inroads into this industrial space. AR-assisted wearables fit perfectly into Industry 4.0 methodologies, and their impact soon became apparent in various industries, from Healthcare to Logistics.
The technology of smart glasses has evolved a lot since their first iterations over ten years ago. We will now see what standard models available on the market can offer regarding features. We will also outline some key differences between standard consumer wearables and smart glasses for the industry. As well as explain how this technology differs from VR.
How does smart glass technology work?
Smart glasses combine Augmented Reality technology into a wearable device that allows hands-free access to the internet. Allowing users to access the internet using voice control allows them to view and listen to up-to-date information on the spot without interrupting their work.
Superimposing information onto a field of vision is one of the key features of AR-assisted smart glasses, and this is achieved through an optical head-mounted display (OHMD) or embedded wireless glasses with transparent heads-up display (HUD), see-through displays, or augmented reality (AR) overlay.
Devices also include a microphone so users can interact with the glasses through voice commands and haptic feedback for manual operation (usually swiping the side of the glasses). An audio output function allows access to audio content, and a rechargeable battery and a processor with memory to access the internet also come as standard.
AR or VR – What’s the difference?
The critical difference between VR viewers and smart glasses is that they work with the existing environment, attempting to add information to help the user navigate it or otherwise assisting them in what they are doing, much like smartphones. Virtual Reality viewing is more of an immersive experience that seeks to take the user to a different space, either for entertainment or convenience.
For example, VR headsets provide flight simulation experiences for pilots or give homebuyers a tour of a house that has not yet been constructed. Smart glasses using AR technology have been designed to be small and lightweight, so users can wear them to perform their daily tasks. In contrast, VR headsets are generally bulky and aren’t designed to be worn for long periods.
How are smart glasses for the industry different from consumer versions?
As noted, smart glasses first came to the market as a consumer product but never captured the popular imagination. The consumer market aims to offer a more convenient way of accessing the internet, focusing on tasks such as shopping, navigating space, and making payments. Design is a crucial consideration for consumer smart glasses, and some of the earlier, more clunky versions may be a key reason their adoption never caught on.
Industrial smart glasses don’t have the same fashion considerations. Still, the hardware needs to be suited to more punishing environments – this means many devices may need to be dustproof and waterproof, have more heavy-duty frames, or be compatible with hard hats.
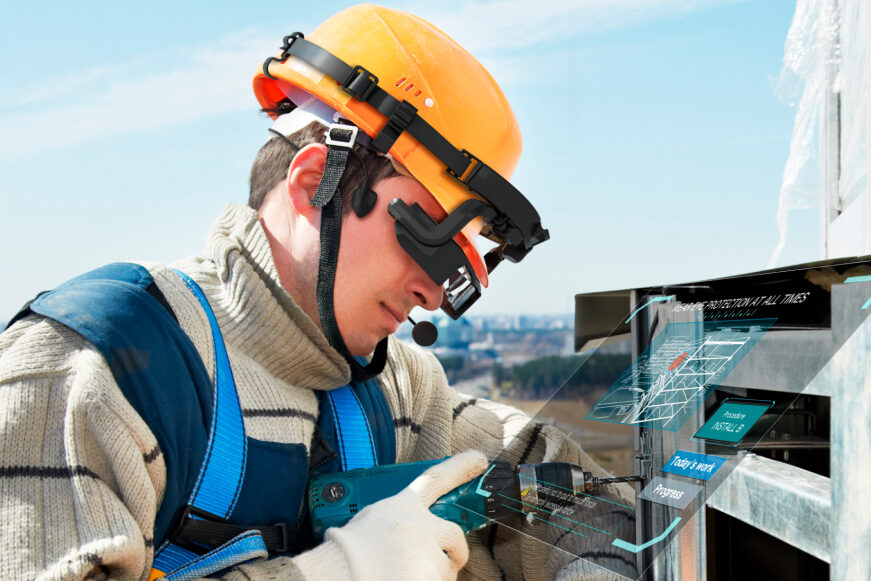

Safety is also a key consideration for glasses for the industrial market, as users may wear them while operating heavy machinery or performing other dangerous tasks. The visual interruption must be minimal, ensuring that information appears in a way that helps but doesn’t hinder the user.
What are some of the main applications of wearable technologies in Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 combines new technologies such as AR and the Internet of Things to improve manufacturing processes. Smart glasses can be integrated with AR technologies to assist industrial processes and offer significant benefits such as increased operational productivity and efficiency and improved quality and accountability.
01. Maintenance
With smart glasses integrated with remote support platforms, remote assistance will be possible. Remote maintenance is faster and more cost-effective as checklists can be easily accessed using smart glasses, and tasks can be performed hands-free. This has the added benefit of improving the safety and standards of these processes.
Learn more about machinery and plant maintenance with remote support
02. Training
In addition, the technology can be used for training purposes; for example, by using smart glasses to watch videos of the equipment maintenance process in real-time or record their work for future training purposes.

Read the case history on “Remote training through the clinician’s eyes”
03. Inspections
Smart glasses can also be used for inspections and audits. The inspector can convert visual data into documents, take photos and videos, and connect with other experts in real-time, all using only voice commands. The expert can then analyze the data and control quality using AR-provided digital graphics and visuals. All of which help to shorten the overall audit periods. It can also be ensured that information is processed correctly and recorded for future reference.
Learn more about AR glasses for field service
What is industrial smart glasses’ future?
The future of AR and smart glasses technology will bring even more benefits to the industrial sector. With improved cameras and hand-eye tracking, users can perform tasks more accurately and improve quality. More durable and lightweight hardware means the technology can be used in a broader range of settings, and advances in processing power mean energy savings that enable hands-free operation for more extended periods – meaning more productivity.
In conclusion, the future looks bright for smart glasses, and their use will likely spread even more widely through the industrial sector as more applications are added. To stay ahead of the competition, companies should stay ahead of trends and look at ways to introduce or further integrate this technology into their processes.
 Giorgio Nepa
Giorgio Nepa